Low-E Glass Market Trends and Forecast
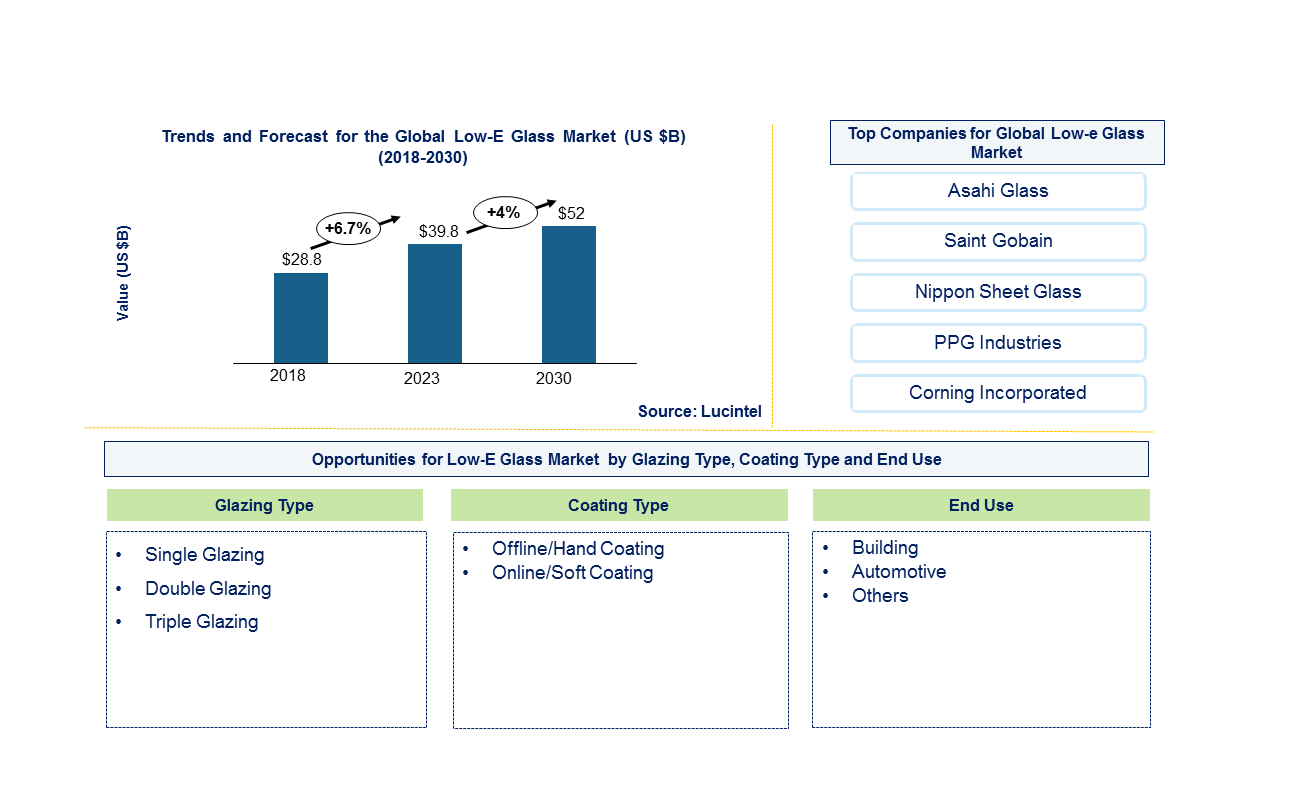
The future of the global low-e glass market looks promising with opportunities in the residential and non-residential construction and automotive industries. The global low-e glass market is expected to reach an estimated $52 billion by 2030, and it is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 4% from 2024 to 2030. The major drivers for this market are growth in construction activities and increasing awareness towards energy saving in residential and non-residential construction industries.
The raw materials used in the global Low-E (low-emissivity) glass market primarily include high-quality float glass, which serves as the base material. Metal oxides, such as silver, tin, and zinc, are used for the thin, transparent coatings that give Low-E glass its energy-efficient properties by reflecting infrared light and reducing heat transfer. Other materials like silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide are also applied in multi-layer coatings to enhance durability, UV resistance, and optical clarity. Advanced chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and magnetron sputtering techniques are employed to apply these coatings uniformly. These materials and processes together help produce low-e glass that significantly improves energy efficiency in buildings.
The price of Low-E glass is generally higher compared to standard clear glass due to its advanced coating technology and energy efficiency benefits. However, it is competitive with other energy-efficient glazing solutions, such as double glazing or tinted glass, offering superior thermal insulation and UV protection. The initial cost of Low-E glass can be offset by long-term energy savings through reduced heating and cooling expenses. Prices also vary based on the type of Low-E coating (hard coat vs. soft coat) and the specific performance characteristics required. Despite the higher upfront cost, the growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency makes Low-E glass a valuable investment for both residential and commercial buildings.
• Lucintel forecasts that double glazing low-e glass will remain the largest segment; it is also expected to witness the highest growth over the forecast period due to growth in non-residential construction and automotive industries.
• Within the global low-e glass market, building will remain the largest end use market; it is also expected to witness the highest growth during the forecast period due to increasing building construction activities and tax incentives in energy efficient upgrades in existing buildings.
• North America is expected to remain the largest region and APAC witness the highest growth over the forecast period supported by increasing urbanization and growth in residential and non-residential construction industry.
Country wise Outlook for the Low E Glass
Major players in the market are expanding their operations and forming strategic partnerships to strengthen their positions. Below image highlights recent developments by major low-e glass producers in key regions: the USA, UK, Germany, China, and India.
Emerging Trends in the Low-E Glass Market
Emerging trends in the low e glass market include:
• Rising Demand from Infrastructure Projects: Large-scale infrastructure projects, such as water and sewage systems, oil and gas pipelines, and urban drainage systems, are driving the demand for large diameter pipes. Urbanization and industrialization in developing countries are significant contributors.
• Growth in Oil & Gas Exploration: The oil and gas industry is a major user of large diameter pipes for transportation and distribution. With ongoing exploration and production activities, especially in regions like North America, the Middle East, and Africa, the demand for these pipes is increasing.
• Adoption of Advanced Materials: There is a shift towards using advanced materials like high-density polyethylene (HDPE), fiberglass reinforced plastic (FRP), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) for large diameter pipes. These materials offer better durability, corrosion resistance, and ease of installation compared to traditional materials like steel and concrete.
• Focus on Sustainability: Environmental concerns are leading to the development and adoption of sustainable piping solutions. Manufacturers are focusing on producing pipes with recyclable materials and lower carbon footprints, aligning with global sustainability goals.
• Technological Innovations: Innovations such as smart piping systems with integrated sensors for monitoring pressure, flow, and leaks are gaining traction. These smart systems enhance operational efficiency, safety, and maintenance capabilities.
• Regulatory Compliance and Standards: Stringent regulatory standards regarding the quality, safety, and environmental impact of large diameter pipes are influencing the market. Compliance with these standards is essential for manufacturers to operate and compete globally.
• Increasing Use of Trenchless Technology: Trenchless technology for the installation and repair of large diameter pipes is becoming more popular due to its cost-effectiveness and minimal disruption to the surface. This method is particularly beneficial in urban areas where excavation can be challenging.
• Cost Reduction and Efficiency: There is a growing emphasis on reducing the overall cost of large diameter pipe systems, including installation, maintenance, and operation. Manufacturers are developing cost-efficient products without compromising on quality and performance.
• Enhanced Corrosion Protection: Corrosion protection technologies, such as coatings and linings, are being increasingly used to extend the lifespan of large diameter pipes, especially in harsh environments like marine and industrial settings.
• Expanding Applications: Beyond traditional uses, large diameter pipes are finding applications in new areas such as renewable energy (e.g., hydroelectric and geothermal systems), district heating and cooling, and industrial processing.
A total of 103 figures / charts and 56 tables are provided in this 215 page report to help in your business decisions. Sample figures with some insights are shown below.
Recent Developments by the Low-E Glass Market
Recent developments in the low-E (low-emissivity) glass market reflect advancements in technology, increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions, and evolving market dynamics. Here are some key updates:
• Nanotechnology: The use of nanotechnology in low-E coatings enhances their performance, improving thermal insulation and reducing glare while maintaining visible light transmittance.
• Multi-Layer Coatings: Development of multi-layer low-E coatings that provide superior energy efficiency by reflecting infrared light while allowing visible light to pass through.
• Electrochromic Glass: Advancements in electrochromic low-E glass that can change tint based on electrical current, allowing for better control of solar heat gain and glare.
• Thermo chromic Glass: Introduction of thermos chromic glass that changes its properties in response to temperature, further improving energy efficiency in varying climates.
• Building Regulations: Stricter building codes and regulations aimed at improving energy efficiency drive the adoption of low-E glass in residential and commercial buildings.
• Sustainability Trends: Increasing awareness of sustainability and energy conservation among consumers and builders promotes the use of low-E glass in new constructions and renovations.
• Automotive Industry: Rising adoption of low-E glass in automotive applications for improved thermal comfort and reduced energy consumption in vehicles.
• Electronics: Growing use of low-E glass in electronics, such as screens and displays, for enhanced energy efficiency and performance.
• Industry Consolidation: Ongoing mergers and acquisitions among manufacturers to expand product offerings and strengthen market presence. For example, acquisitions focused on enhancing technology capabilities in low-E glass production.
• Joint Ventures: Collaborations between glass manufacturers and technology firms to develop innovative low-E glass solutions and explore new applications.
• Research Initiatives: Partnerships with research institutions to advance low-E glass technologies and improve energy efficiency ratings.
• Green Building Initiatives: Increased government incentives and programs supporting green building initiatives drive demand for low-E glass in residential and commercial construction.
• Market Growth: Significant growth in the low-E glass market, supported by a rising focus on energy-efficient buildings.
• Sustainability Regulations: Stringent regulations in the European Union promoting energy-efficient building practices contribute to the growing adoption of low-E glass.
• Innovation Hubs: Establishment of innovation hubs focusing on sustainable construction materials, including low-E glass.
• Cost-Effectiveness: Studies highlighting the long-term cost savings associated with low-E glass installations through reduced heating and cooling expenses.
• Environmental Impact: Low-E glass contributes to lower carbon footprints by reducing energy consumption in buildings, aligning with global sustainability goals.
• Raw Material Availability: Fluctuations in the availability and cost of raw materials used in low-E glass production can impact pricing and production capacity.
• Logistics and Distribution: Ongoing logistics challenges in the supply chain due to geopolitical factors and pandemic-related disruptions.
These developments showcase the dynamic nature of the low-E glass market, driven by technological innovations, regulatory changes, and a growing emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency.
Strategic Growth Opportunities for Low-E Glass Market
Strategic growth opportunities in the low-E glass market are shaped by increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions, advancements in technology, and evolving building regulations. Here are key areas for growth:
Rising Demand for Energy Efficiency
• Green Building Initiatives: Growing emphasis on sustainable construction practices and energy-efficient buildings creates demand for low-E glass as a key component in reducing energy consumption.
• Regulatory Standards: Stricter energy codes and regulations promoting energy-efficient windows drive market growth for low-E glass products.
Technological Advancements
• Innovative Coatings: Development of advanced low-E coatings that enhance performance, such as improved solar control and UV protection, attracting more customers.
• Smart Glass Technologies: Integration of low-E glass with smart technologies that allow for dynamic control of solar gain and daylighting, offering added value in commercial and residential applications.
Expanding Application Areas
• Commercial Construction: Increased construction of commercial buildings, such as offices and retail spaces, presents significant opportunities for low-E glass installations.
• Residential Renovation: Growth in home renovation projects focusing on energy efficiency provides a lucrative market for retrofitting homes with low-E glass windows.
Emerging Markets
• Asia-Pacific Growth: Rapid urbanization and increasing disposable incomes in countries like China and India drive demand for energy-efficient building materials, including low-E glass.
• Infrastructure Development: Investments in infrastructure and real estate development in emerging economies create new opportunities for low-E glass products.
Sustainability Trends
• Recycling and Eco-Friendly Practices: Increasing focus on sustainability and recycling in the construction industry promotes the use of low-E glass as an environmentally friendly building material.
• Lifecycle Assessments: Conducting lifecycle assessments to highlight the long-term energy savings and reduced carbon footprint of low-E glass compared to traditional glass options.
Collaborative Partnerships
• Industry Collaborations: Collaborating with architects, builders, and energy consultants to promote low-E glass as part of energy-efficient building solutions.
• Joint Ventures with Technology Firms: Partnering with technology companies to develop integrated solutions that enhance the functionality of low-E glass in smart buildings.
Consumer Awareness and Education
• Marketing Campaigns: Educating consumers and builders about the benefits of low-E glass in terms of energy savings, comfort, and aesthetics.
• Demonstrating ROI: Providing case studies and data that demonstrate the return on investment (ROI) for low-E glass in reducing energy bills and improving indoor environments.
Product Diversification
• Expanded Product Range: Developing a wider variety of low-E glass products, such as laminated, tempered, and insulated glass units, to cater to different market segments.
• Customization Options: Offering customizable solutions tailored to specific architectural needs and aesthetic preferences.
The low-E glass market is poised for growth driven by energy efficiency demands, technological innovations, and expanding applications. By focusing on sustainability, emerging markets, and collaborative partnerships, companies can effectively capitalize on these opportunities and enhance their market positioning.
Low-E Glass Market Driver and Challenges
Drivers in the Low-E Glass Market
1. Growing Demand for Energy Efficiency
Increasing focus on reducing energy consumption in buildings drives demand for low-E glass, which helps minimize heat loss and gain.
2. Regulatory Standards
Stricter building codes and energy efficiency regulations worldwide promote the adoption of low-E glass in both residential and commercial construction.
3. Sustainability Trends
A shift towards sustainable construction practices encourages the use of low-E glass as an eco-friendly option that contributes to lower carbon footprints.
4. Advancements in Technology
Innovations in low-E coatings and glazing technologies enhance the performance of low-E glass, making it more appealing to architects and builders.
5. Increased Construction Activities
Growth in the construction industry, particularly in emerging markets, creates significant opportunities for low-E glass applications in new buildings.
6. Consumer Awareness
Rising awareness among consumers about the benefits of energy-efficient windows encourages more homeowners to choose low-E glass for renovations and new builds.
Challenges in the Low-E Glass Market
1. High Initial Costs
The higher upfront cost of low-E glass compared to traditional glass can deter some consumers and builders, especially in price-sensitive markets.
2. Market Competition
Intense competition from alternative glazing options, such as tinted or reflective glass, can limit market share for low-E glass products.
3. Supply Chain Issues
Disruptions in the supply chain, including raw material shortages and logistical challenges, can impact the availability and cost of low-E glass.
4. Installation Challenges
The need for specialized installation techniques and trained professionals can pose challenges for widespread adoption, particularly in regions with limited expertise.
5. Regulatory Changes
Evolving regulations and standards may create uncertainty in the market, making it difficult for manufacturers to adapt quickly and comply.
6. Perceived Performance Limitations
Some consumers may have misconceptions about the performance of low-E glass in terms of visibility, aesthetics, or durability, affecting their purchasing decisions.
The low-E glass market is driven by a strong demand for energy efficiency and sustainability, supported by technological advancements and regulatory frameworks. However, challenges such as high costs, market competition, and installation issues must be addressed to fully capitalize on growth opportunities.
Low-E Glass Suppliers and their Market Shares
In this globally competitive market, several key players such as Asahi Glass, Saint-Gobain, Nippon Sheet Glass, Xinyui Glass Holdings, PPG Industries, etc. dominate the market and contribute to industry’s growth and innovation. These players capture maximum market share. To know the current market share of each of major players contact us.
Companies in the market compete on the basis of product quality offered. Major players in this market focus on expanding their manufacturing facilities, R&D investments, infrastructural development, and leverage integration opportunities across the value chain. With these strategies low-e glass companies cater increasing demand, ensure competitive effectiveness, develop innovative products & technologies, reduce production costs, and expand their customer base. Some of the low-e glass companies profiled in this report includes.
• Asahi Glass
• Saint-Gobain
• Nippon Sheet Glass
• Xinyui Glass Holdings
• PPG Industries
• CSG Holdings
• Taiwan Glass Industries
• Corning Incorporated
These companies have established themselves as leaders in the low-e glass industry, with extensive product portfolios, global presence, and strong research and development capabilities. They continually strive to enhance their market positions through strategic partnerships, mergers and acquisitions, and product innovations.
The market share dynamics within the low-e glass are evolving, with the entry of new players and the emergence of innovative low-e glass technologies. Additionally, collaborations between material suppliers, manufacturers, and end-users are fostering technological advancements and expanding market opportunities.
Low-E Glass Market by Segments
The major segments of Low-E (low-emissivity) glass that are experiencing significant growth include architectural and automotive applications. In architecture, there is a rising demand for energy-efficient building materials to comply with stringent environmental regulations and achieve sustainability certifications. Low-E glass offers superior thermal insulation, reducing heating and cooling costs while enhancing occupant comfort. The trend towards green building practices and smart cities further drives the adoption of Low-E glass in residential, commercial, and institutional construction projects worldwide. In the automotive sector, there is increasing integration of Low-E glass in vehicle windows to improve cabin comfort, reduce HVAC load, and enhance fuel efficiency. This segment is propelled by automotive manufacturers' focus on light weighting vehicles and meeting stringent emission standards. Overall, the growth of Low-E glass is fueled by its ability to contribute to energy savings, environmental sustainability, and enhanced performance across diverse applications in both building and automotive industries.
This low-e glass market report provides a comprehensive analysis of the market's current trends, growth drivers, challenges, and future prospects in all major segments like above. It covers various segments, including end use, glazing, and coating type. The report offers insights into regional dynamics, highlighting the major markets for low-e glass and their growth potentials. The study includes trends and forecast for the global low-e glass market by end use, glazing, coating type and region as follows:
Low-E Glass Market By End Use Industry [Value ($ Million) and Volume (Million Square Meter) from 2018 to 2030]:
• Building
o Residential
o Education
o Office
o Healthcare
o Hospitality
o Retail
• Automotive
• Others
Low-E Glass Market By Glazing [Value ($ Million) from 2018 to 2030]:
• Single Glazing
• Double Glazing
• Triple Glazing
Low-E Glass Market By Coating Type [Value ($ Million) from 2018 to 2030]:
• Offline/Hard Coating
• Online/Soft Coating
Low-E Glass Market By Region [Value ($ Million) and Volume (Million Square Meter) from 2018 to 2030]:
• North America
• Europe
• APAC
• ROW
Features of the Low-E Glass Market
• Market Size Estimates: Low-e glass market size estimation in terms of value ($M).
• Trend and Forecast Analysis: Market trends (2018-2023) and forecast (2024-2030) by various segments and regions.
• Segmentation Analysis: Low-e glass market size by various segments, such as coating type, glazing, and end use industry.
• Regional Analysis: Low-e glass market breakdown by North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Rest of the World.
• Growth Opportunities: Analysis on growth opportunities in different coating type, glazing, end use industry, and regions for low-e glass market.
• Strategic Analysis: This includes M&A and competitive landscape for the low-e glass.
• Analysis of competitive intensity of the industry based on Porter’s Five Forces model.
If you are looking to expand your business in low-e glass or adjacent markets, then contact us. We have done hundreds of strategic consulting projects in market entry, opportunity screening, due diligence, supply chain analysis, M & A, and more.
FAQ
Q1. What is the low-e glass market size?
Answer: The global low-e glass market is expected to reach an estimated $52 billion by 2030.
Q2. What is the growth forecast for low-e glass market?
Answer: The low-e glass market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 4% from 2024 to 2030.
Q3. What are the major drivers influencing the growth of the low-e glass market?
Answer: The major drivers for this market are growth in construction activities and increasing awareness towards energy saving in residential and non-residential construction industries.
Q4. What are the major applications or end use industries for low-e glass?
Answer: Building and automotive are the major end use for low-e glass.
Q5. What are the emerging trends in low-e glass market?
Answer: Emerging trends which have a direct impact on the dynamics of the market include innovations such as smart piping systems with integrated sensors for monitoring pressure, flow, and leaks are gaining traction. These smart systems enhance operational efficiency, safety, and maintenance capabilities.
Q6. Who are the key low-e glass companies?
Answer: Some of the key low-e glass companies are as follows:
• Asahi Glass
• Saint-Gobain
• Nippon Sheet Glass
• Xinyui Glass Holdings
• PPG Industries
• CSG Holdings
• Taiwan Glass Industries
• Corning Incorporated
Q7.Which low-e glass product segment will be the largest in future?
Answer: Lucintel forecasts that double glazing low-e glass will remain the largest segment; it is also expected to witness the highest growth over the forecast period due to growth in non-residential construction and automotive industries.
Q8: In low-e glass market, which region is expected to be the largest in next 5 years?
Answer: North America will remain the largest region and is expected to witness the highest growth over next 5 years.
Q9. Do we receive customization in this report?
Answer: Yes, Lucintel provides 10% Customization Without any Additional Cost.
This report answers following 11 key questions
Q.1 What are some of the most promising potential, high-growth opportunities for the low-e-glass market by glazing (single glazing, double glazing, and triple glazing), end use industry (building, automotive, and other end use), coating type (offline/hard coating and online/soft coating), and region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Rest of the World)?
Q.2 Which segments will grow at a faster pace and why?
Q.3 Which regions will grow at a faster pace and why?
Q.4 What are the key factors affecting market dynamics? What are the drivers and challenges of the water storage tank market?
Q.5 What are the business risks and threats to the low-e-glass market?
Q.6 What are emerging trends in this low-e-glass market and the reasons behind them?
Q.7 What are some changing demands of customers in the low-e-glass market?
Q.8 What are the new developments in the low-e-glass market? Which companies are leading these developments?
Q.9 Who are the major players in the low-e-glass market? What strategic initiatives are being implemented by key players for business growth?
Q.10 What are some of the competitive products and processes in the low-e-glass market, and how big of a threat do they pose for loss of market share via material or product substitution?
Q.11 What M&A activities did take place in the last five years in the low-e-glass market?
For any questions related to low-e-glass market or related to low-e-glass market share, low-e-glass market analysis, low-e-glass market size, and low-e-glass manufacturers, write to Lucintel analysts at helpdesk@lucintel.com. We will be glad to get back to you soon.